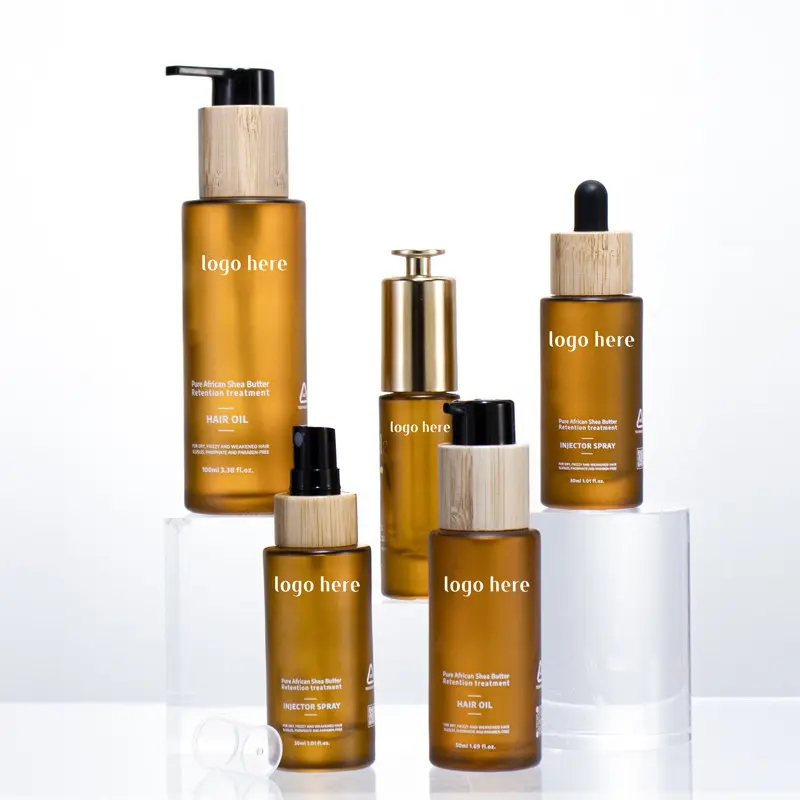
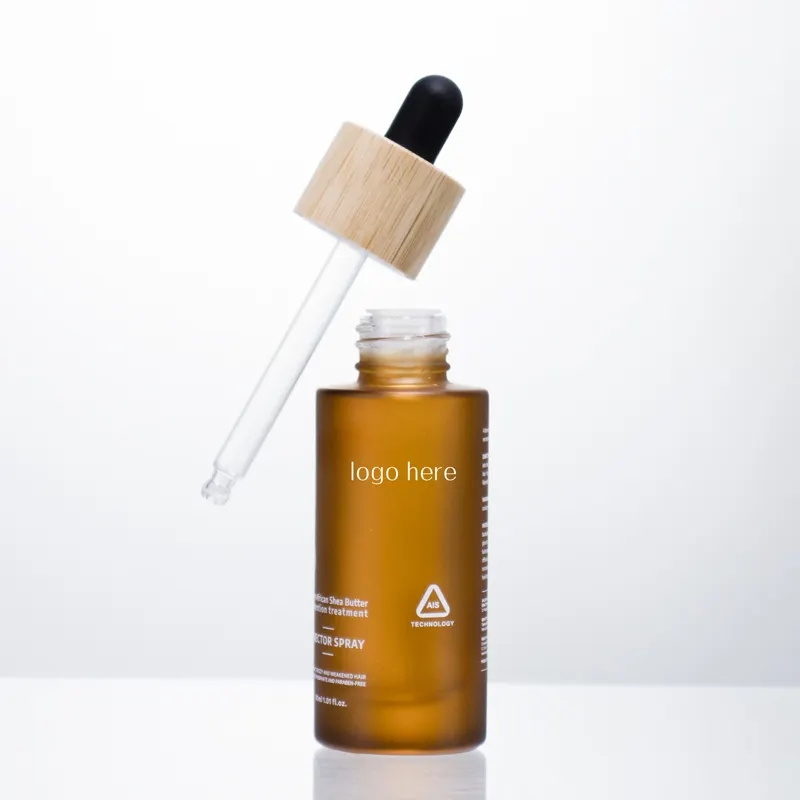
Plastic cosmetic bottles boast several distinctive features and advantages. Firstly, they are lightweight and durable, making them convenient for travel and everyday use, thus serving as an ideal choice. Secondly, plastic bottles offer high transparency, showcasing product colors and textures, facilitating consumer observation and selection. Moreover, plastic cosmetic bottles have relatively low manufacturing costs and versatile production processes, allowing for diverse shapes and sizes to meet market demands. Additionally, plastic bottles effectively shield products from environmental factors, extending their shelf life. However, it’s essential to note potential environmental pollution and sustainability concerns associated with plastic bottles. Thus, it’s crucial to consider recycling and reusability schemes to minimize adverse environmental impacts while using them.
Cosmetic bottles are commonly made from various types of plastics:
- Polyethylene (PE): Polyethylene includes High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). Both offer toughness and durability. HDPE is often used for sturdy bottles, while LDPE suits more flexible bottle bodies.
- Polypropylene (PP): PP possesses excellent chemical stability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for housing cosmetic products. It’s frequently used for bottle caps or squeezable bottle bodies.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): PET is transparent, corrosion-resistant, and commonly used for showcasing products, such as clear bottles for liquid cosmetics.
- Polycarbonate (PC): PC offers high transparency and heat resistance, making it suitable for packaging heat-sensitive products like cosmetics with higher temperature ingredients.
- Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC): PVDC is often added as a barrier layer within plastic bottles to protect cosmetics from oxygen and moisture.
These materials each have their own advantages and drawbacks. Material selection often depends on the product’s characteristics such as chemical properties, stability, transparency, and the required protective functions.